What is QuickMind®? A Guide to the FDA-Cleared VR Cognitive Health System
2025-11-043 ways QuickMind boosts your brain health fast
2025-11-17
Virtual reality is reshaping rehabilitation for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease. Advanced systems like QuickMind® use artificial intelligence, eye-tracking, and remote access to deliver personalized cognitive therapy. Recent studies show that these technologies improve early detection and assessment of cognitive impairment, making therapy more engaging and objective. Patients and caregivers benefit from home-based training and clear progress tracking. The table below highlights the impact of VR interventions:
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample Size | 362 Alzheimer’s disease patients participated in the studies reviewed. |
| Improvements | VR interventions showed enhancements in cognition, memory, executive function, and physical balance. |
| Study Inclusion | Eight out of 2,023 studies were included in the systematic review. |
Key Takeaways
- VR rehabilitation systems like QuickMind® use advanced technology to provide personalized cognitive therapy for Alzheimer’s patients.
- These systems improve cognitive functions, memory, and physical balance, enhancing overall quality of life.
- Patients benefit from home-based training, allowing for flexible therapy sessions and clear progress tracking.
- VR therapy fosters emotional connections and social engagement, reducing feelings of isolation for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
- The immersive nature of VR increases patient motivation and engagement, leading to better rehabilitation outcomes.
VR rehabilitation systems overview
Core components and technology
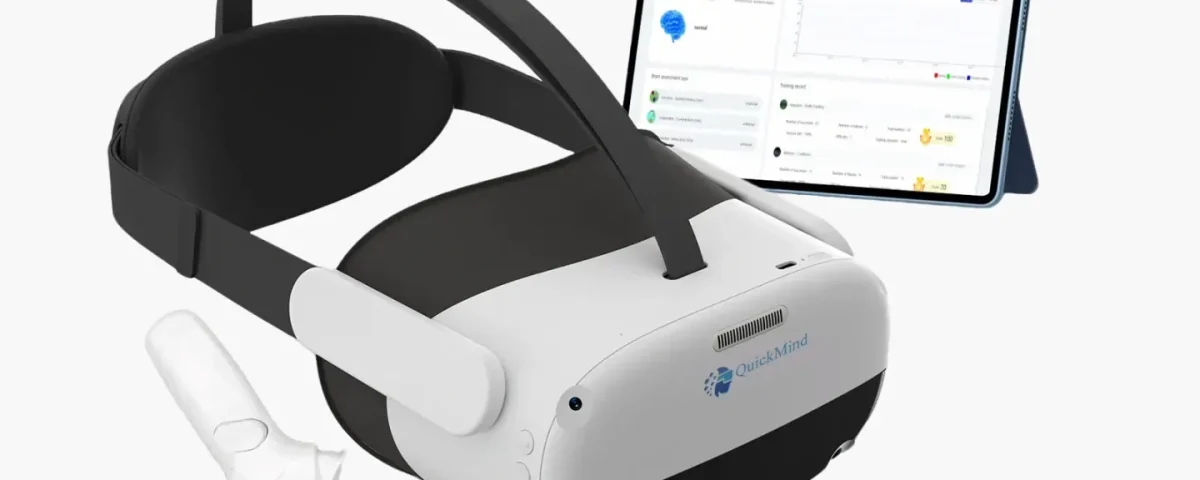
Modern VR rehabilitation systems combine advanced hardware and intelligent software to deliver effective therapy. QuickMind® and Yiwei Medical lead the field with their innovative platforms. These systems use artificial intelligence, eye-tracking, and cloud computing to personalize therapy for each user. QuickMind® stands out with FDA clearance, ensuring reliability and safety for clinical and home use.
The table below outlines the main technological components found in leading VR rehabilitation systems:
| Component Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Devices | Includes joysticks, gloves, surfaces, 3D head-mounted displays (HMDs), audio headsets, speakers, etc. |
| Interaction Methods | Patients can interact from egocentric or allocentric points of view, enhancing engagement in VR. |
| Sensory Stimulation | Utilizes visual, tactile, and kinesthetic stimuli to create a multisensory experience for patients. |
| Immersion Features | Number of stimulated senses, interaction levels, synthetic stimuli fidelity, and isolation from external stimuli. |
These systems also gather and transmit patient performance data. They collect psycho-physiological information, such as heart rate variability and respiration. Real-time feedback allows clinicians to adjust therapy instantly, supporting optimal outcomes.
Applications in cognitive health
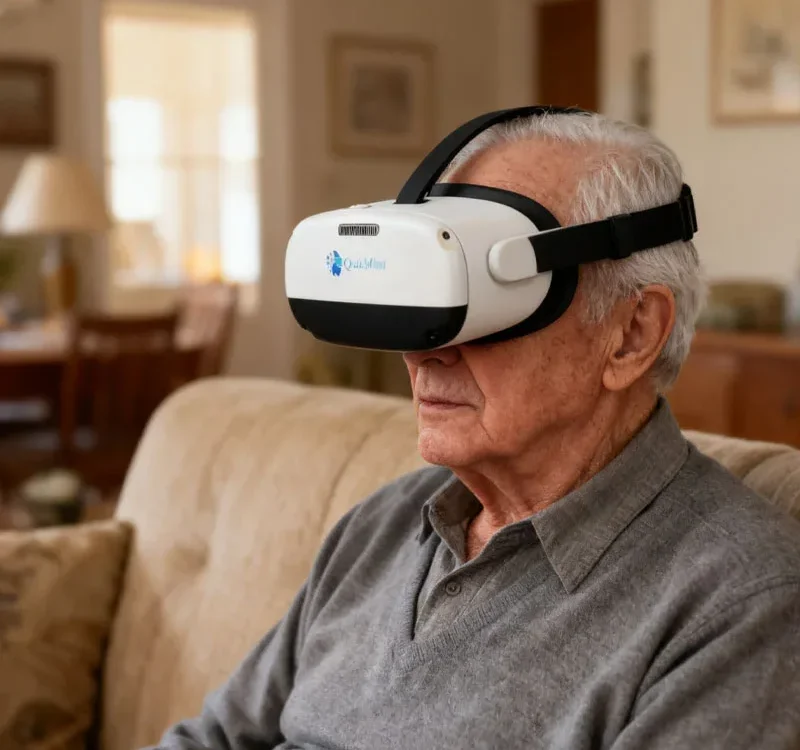
VR rehabilitation systems play a vital role in cognitive health, especially for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. QuickMind® delivers rapid cognitive screenings and personalized rehabilitation plans. The system uses immersive environments and interactive tasks to stimulate memory, attention, and executive function. Patients benefit from both clinic-based and home-based flexibility, making therapy accessible and convenient.
Yiwei Medical’s platform extends care across the entire brain health journey. Their solutions support ultra-early screening, precise diagnosis, and ongoing rehabilitation. Both platforms provide quantifiable progress tracking, helping clinicians and caregivers monitor improvements over time. These features make VR rehabilitation a powerful tool for enhancing cognitive health and supporting long-term care.
VR for Alzheimer’s disease rehabilitation
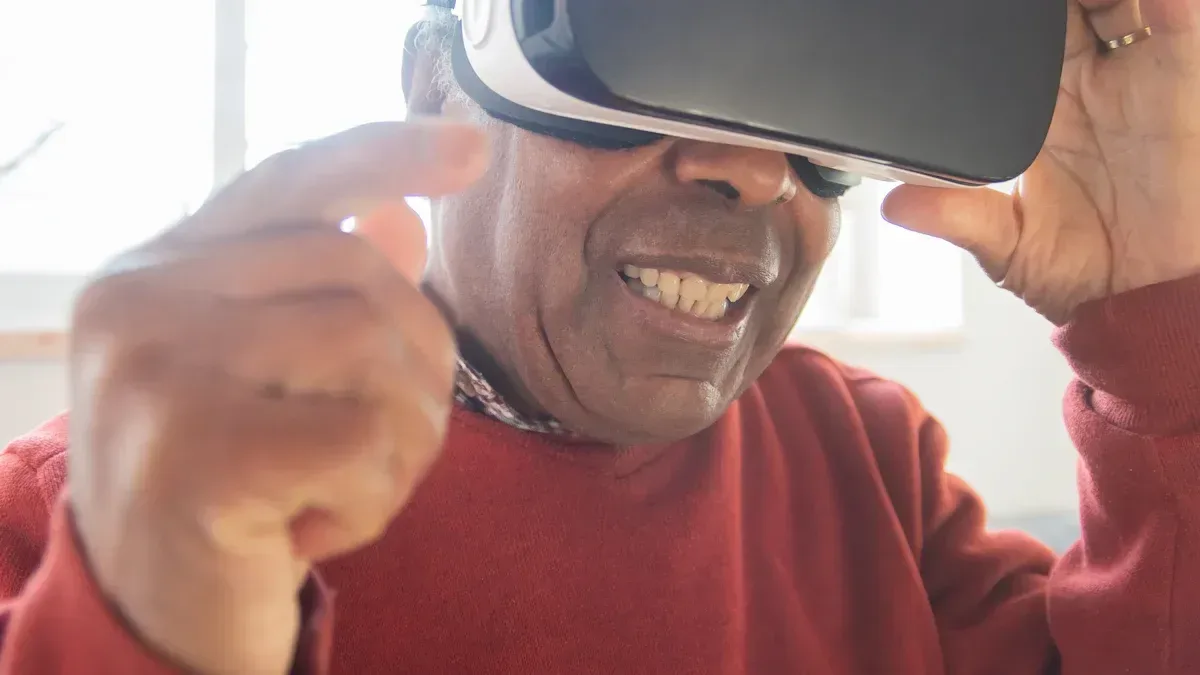

Cognitive training and memory support
Virtual reality systems offer immersive environments that stimulate cognitive functions in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. These platforms deliver interactive tasks that challenge memory, attention, and executive function. QuickMind® and similar systems use AI-driven personalization to adapt therapy to each patient’s needs. This approach helps maintain engagement and supports measurable progress.
Research highlights several benefits of VR-based cognitive training for Alzheimer’s disease:
- VR-based training improved functional independence in daily activities, such as cooking.
- The immersive and interactive nature of VR enhances cognitive skills and memory retention.
- Patients who participated in VR sessions showed sustained improvements in work performance over time.
A clinical trial involving patients with mild cognitive impairment, a condition often preceding Alzheimer’s disease, demonstrated significant gains:
| Study | Participants | Intervention | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Effectiveness of VR-Based Cognitive Training Program for Mild Cognitive Impairment | 32 patients with MCI | 12-week VR training program, twice-weekly sessions | Significant improvements in neuropsychological test scores and brain connectivity in memory-related regions. |
Additional studies confirm that VR technology benefits those managing cognitive disorders. In a series of trials, subjects receiving VR-based training showed notable improvements in long-term memory recall. These findings suggest that VR interventions can enhance cognitive functions and support daily living for people with Alzheimer’s disease.
Virtual reality rehabilitation also positively influences executive functions and attention. Patients engage in interactive tasks that stimulate cognitive areas and provide real-time feedback. This process helps them switch between tasks more effectively and improves their ability to manage daily activities.
Physical and mobility benefits
VR rehabilitation systems extend beyond cognitive support by addressing physical and mobility challenges associated with Alzheimer’s disease. These platforms create safe, controlled environments where patients can practice motor skills and balance exercises. The gamified nature of VR encourages longer participation and increases motivation.
Clinical studies demonstrate the physical benefits of VR interventions:
| Study | Findings |
|---|---|
| Fenney and Lee (2010) | Improved memory in dementia patients through bowling on Nintendo Wii. |
| Yamaguchi et al. (2011) | Enhanced cognitive levels with upper and lower limb exergaming tasks. |
| Flynn et al. (2003) | Improved gait and balance using Wii Fit compared to normal walking tasks. |
Further research supports the impact of VR on body balance and motor skills:
| Study | Findings |
|---|---|
| Kwan et al. (2021) | VR enhances cognitive-motor interventions, leading to quicker steps and potentially preventing falls. |
| Torpil et al. (2021) | Serious games improved visuospatial perception, organization, attention, and concentration. |
| Zhu et al. (2021) | Systematic review showed moderate impact of VR on cognitive and motor functions, including balance. |
| Gao et al. (2021) | Significant improvements in cognition and attention, though not in motor function. |
| Pichierri et al. (2011) | Computerized interventions showed positive effects on physical abilities in older adults. |
| Schoene et al. (2014) | VR environments with treadmills reported improvements in balance and mobility. |
VR technology allows patients to safely experience outdoor environments while exercising. This approach leads to increased positive emotions and decreased negative emotions. Patients often feel more motivated to participate in physical training, which can help maintain independence and reduce the risk of falls.
Emotional and social engagement
Emotional well-being and social interaction play a crucial role in the quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. VR therapy creates immersive experiences that foster emotional connections and social engagement. Patients can revisit familiar places, interact with virtual companions, and share joyful moments with caregivers.
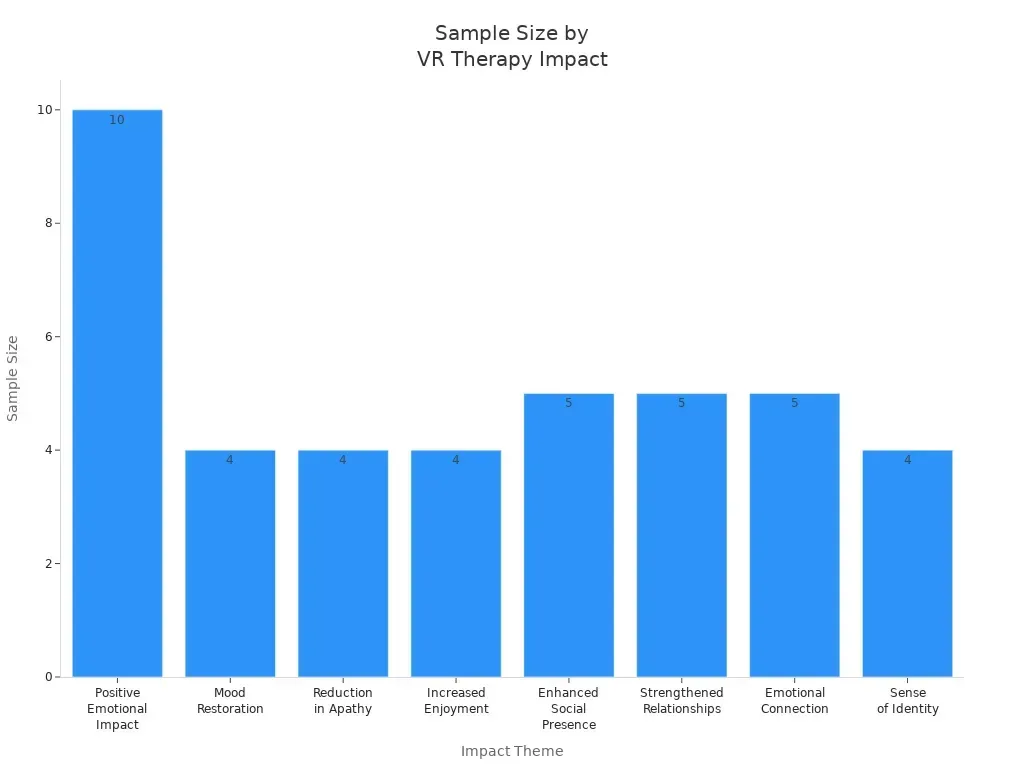
A range of studies highlights the emotional and social benefits of VR therapy:
| Theme/Impact | Description | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Emotional Impact | Reductions in anxiety and depression, enhanced emotional connections, and overall engagement in immersive environments. | n = 10 |
| Mood Restoration | VR therapy contributes to restoring mood and reducing anxiety. | n = 4 |
| Reduction in Apathy | Significant reduction in apathy levels observed through quantitative measures. | n = 4 |
| Increased Enjoyment | Users found VR sessions enjoyable and engaging. | n = 4 |
| Enhanced Social Presence | VR promotes social interactions and shared experiences. | n = 5 |
| Strengthened Relationships | Improved communication and shared joyful experiences between caregivers and residents. | n = 5 |
| Emotional Connection | Leveraging nostalgia and emotional engagement for mental health improvements. | n = 5 |
| Sense of Identity | VR helps maintain a sense of self-worth and personal identity. | n = 4 |
Personalized and remote-access VR interventions further enhance social interaction. These systems provide tailored cognitive stimulation and AI-powered companionship. Participants report improved quality of life and reduced feelings of isolation. The ability to connect with others, even virtually, helps maintain a sense of identity and belonging for those living with Alzheimer’s disease.
Key benefits for Alzheimer’s disease patients
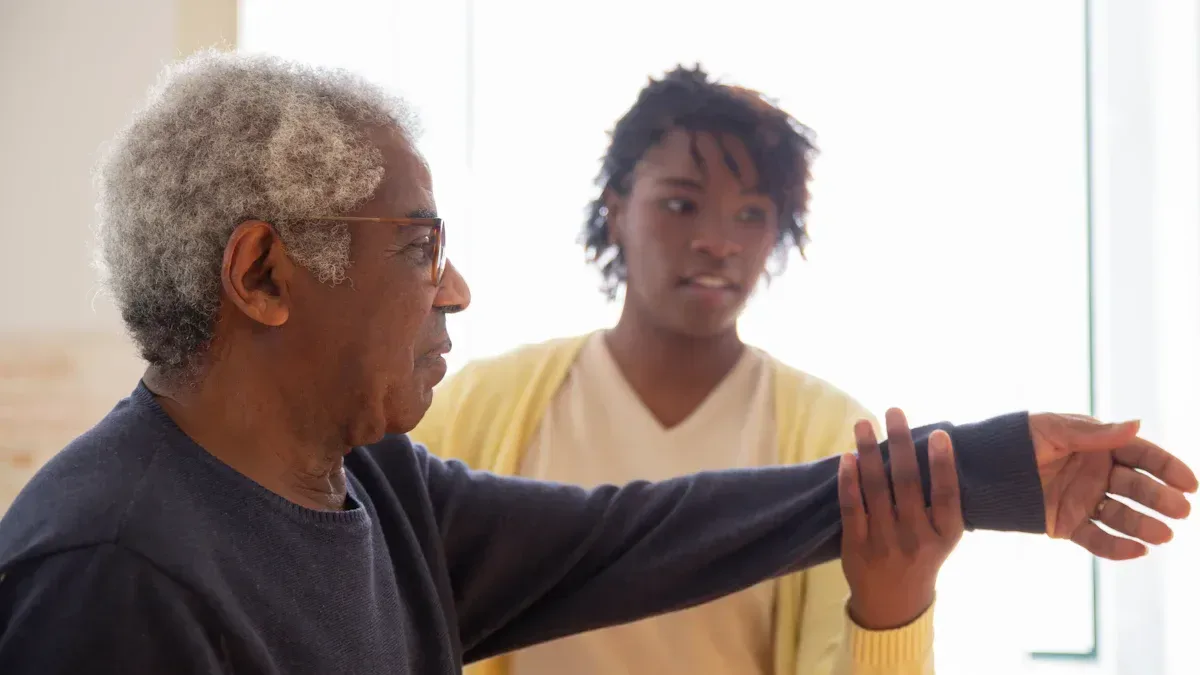

Personalization and adaptability
VR rehabilitation systems provide a high level of personalization for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. These platforms use artificial intelligence to create tailored environments and adaptive learning experiences. The technology analyzes speech, emotional cues, and patient preferences to deliver context-specific therapy. Modular content allows therapists to adjust scenarios, ensuring each session matches the patient’s needs and interests.
| Evidence Description | Details |
|---|---|
| AI-enabled conversations and personalized environments | Enhances cognitive rehabilitation efficacy for patients with cognitive disorders. |
| Tailored AI assistant’s adaptive learning | Offers context-specific and patient-specific dialogue through speech analysis and emotional cues. |
| Modular content architecture | Allows personalization of virtual scenarios to align with patient preferences. |
| AI companion understanding speech, memories, emotions | Creates authentic interactions that help combat loneliness and cognitive decline. |
Therapists can design rehabilitation programs that address both cognitive and physical needs. The adaptability of VR ensures exercises remain challenging yet achievable, which helps foster a sense of accomplishment.
Safe, controlled environment
Safety remains a top priority in VR rehabilitation. These systems create controlled environments where patients can practice skills without real-world risks. Clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and tolerability of VR-based interventions for Alzheimer’s disease.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Type | Single-blind, sham-controlled clinical trial |
| Objective | Evaluate safety, tolerability, and feasibility of VR-based audiovisual stimulation for Alzheimer’s patients |
| Participants | 50 participants (25 with mild AD or MCI due to AD, 25 cognitively healthy) |
| Intervention | Audiovisual stimulation via VR headset |
| Evaluation Methods | EEG and questionnaires for safety and tolerability |
Controlled VR settings allow patients to engage in real-world simulations, such as crossing a street or preparing a meal, without exposure to hazards. Gamified tasks and immersive environments also provide distraction-based therapies, reducing discomfort and increasing patient comfort.
Motivation and engagement
VR technology increases motivation and engagement among patients. The immersive nature of VR encourages longer and more intense participation in therapy. Patients often prefer activities that reflect their interests or allow them to reminisce, which leads to higher engagement.
- VR boosts patient motivation and engagement with treatment.
- Patients train longer and with greater intensity, improving rehabilitation outcomes.
- Immersive experiences provide a welcome distraction, making therapy enjoyable and stimulating.
- Participants show a strong preference for VR activities that connect with their memories and interests.
- Feedback confirms the usability and appeal of VR interventions for individuals with dementia.
Home-based and clinic-based flexibility, along with data-driven care and progress tracking, make VR rehabilitation convenient and effective. These features support increased participation and help patients maintain independence.
Challenges and future directions
Accessibility and cost
Access to VR rehabilitation remains limited for many patients. High costs often prevent those in need from obtaining advanced therapies. Insurance coverage and reimbursement policies play a significant role. Many patients cannot afford VR technology without insurance support. Providers also face challenges, as low reimbursement rates make it difficult to justify investment in these systems. Additional barriers include discomfort from headset fit, difficulty using headsets with glasses, and concerns about appearance. Some users experience limited immersion or interaction, and the lack of dementia representation in content can reduce engagement. Stigmatization and high costs further restrict widespread adoption.
Note: Expanding insurance coverage and developing cost-effective solutions will help more patients benefit from VR rehabilitation.
Usability for older adults
Older adults encounter unique usability challenges with VR systems. Reduced working memory, attention, and computer literacy can make learning new technology difficult. Physical limitations, such as slower motor speed and decreased hand-eye coordination, also impact their experience. Vision and hearing changes add to these challenges. Overloading executive functions with complex input devices can lead to poorer memory performance. Designers address these issues by focusing on user-centered design. They create accessible and comfortable applications, provide regular feedback, and ensure stable visual targets. Improvements in hardware ergonomics and intuitive software interfaces help older adults use VR more effectively. Social interaction features in VR can also reduce feelings of isolation.
Research, effectiveness, and innovation
Current research on VR rehabilitation shows promise but faces several gaps. Many studies have small sample sizes and short intervention periods, which limits the reliability of results. The absence of randomized control groups makes it difficult to establish clear cause-and-effect relationships. Emerging technologies offer new opportunities. Artificial intelligence and adaptive learning algorithms allow real-time adjustments in therapy, optimizing cognitive load and maximizing therapeutic benefits. Real-time data analytics improve monitoring and intervention strategies. Combining VR with traditional therapies enhances daily living skills and neural efficiency. Practitioners benefit from increased efficiency, but legal and ethical considerations must be addressed as AI becomes more integrated into care.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time Adjustments | AI enables dynamic changes in therapy based on patient performance. |
| Personalized Treatment | AI tools create individualized rehabilitation plans. |
| Data Analytics | Real-time analytics support better monitoring and intervention. |
| Synergistic Benefits | VR combined with traditional training improves daily function. |
| Practitioner Efficiency | AI increases efficiency for healthcare providers. |
| Challenges | Legal and ethical issues require careful consideration. |
The future of VR rehabilitation depends on continued research, improved accessibility, and thoughtful integration of new technologies.
VR rehabilitation systems, including advanced platforms like QuickMind®, transform Alzheimer’s disease care by improving cognitive and physical abilities, engagement, and safety. These systems deliver immersive experiences that enhance memory, skill transfer, and daily living.
| Benefit | VR Rehabilitation Systems | Traditional Therapy Approaches |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement of Cognitive Domains | Engages multiple cognitive domains simultaneously | Typically focuses on specific cognitive areas |
| Enhancement of Cognitive Function | Demonstrated positive outcomes in cognitive functioning | Improvements may vary based on individual therapy |
| Immersive Experience | Provides immersive environments for interaction | Limited to real-world settings and interactions |
| Ecological Validity | Simulates real-life scenarios for assessment | Standard tests may lack ecological validity |
Challenges remain, such as high costs and technical complexity. Future innovations will focus on personalized care and deeper clinical integration. Many caregivers and professionals believe VR can improve communication, reduce anxiety, and support mental health. The promise of VR in Alzheimer’s care continues to grow, offering hope for better outcomes.
FAQ
What is a VR rehabilitation system for Alzheimer’s disease?
A VR rehabilitation system uses virtual reality technology to deliver cognitive and physical therapy. These systems create immersive environments that help patients practice memory, attention, and motor skills in a safe and engaging way.
How does QuickMind® personalize therapy for each patient?
QuickMind® uses artificial intelligence and eye-tracking to assess cognitive function. The system adapts therapy tasks based on individual performance, ensuring each patient receives a tailored rehabilitation plan.
Can patients use VR rehabilitation systems at home?
Yes. Many VR rehabilitation systems, including QuickMind®, offer home-based versions. Patients can complete therapy sessions remotely, and clinicians can monitor progress through cloud-based data tracking.
Are VR rehabilitation systems safe for older adults?
Clinical studies show that VR rehabilitation systems are safe and well-tolerated by older adults. The technology provides a controlled environment, reducing the risk of falls or injury during therapy.
What benefits do caregivers gain from VR rehabilitation systems?
Caregivers receive quantifiable progress reports and remote access to therapy data. This support helps them track improvements, adjust care plans, and reduce the burden of in-person supervision.





